Image processing with Python and SciPy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 278: | Line 278: | ||
As long as the images have the same size you can sum them by simple addition | As long as the images have the same size you can sum them by simple addition | ||
sum_image = image1 + image2 + | sum_image = image1 + image2 + image3 ... | ||
We would do this to create a final image that is effectively one long exposure, the sum of all the contributing image exposure times. Because of guiding errors, cosmic rays, and weather one very long exposure is often not possible, but 10's or 100's of shorter exposures can be "co-added" after selecting the best ones and aligning them so that each pixel in the contributing image corresponds to the same place in the sky. | |||
Finally, for spectroscopy the useful data in an image may be a sum over a region. In that case we could index through the array and explicitly create the sum if needed, but in the ideal case of a spectrum we may want only the sum along a column for each element of a row. For that, the function is | |||
spectrum = np.sum(image, axis) | |||
which returns a numpy array that is the sum along the specified axis. If there are regions in the image that should not be included in the sum, then the image could be masked before computing the sum. The result is a 1-d array in which each element is the signal at a different wavelength. | |||
== FITS headers == | == FITS headers == | ||
Revision as of 04:21, 28 February 2013
Given that NumPy provides multidimensional arrays, and that there is core support through the Python Imaging Library and Matplotlib to display images and manipulate images in the Python environment, it's easy to take the next step and combine these for scientific image processing. As part of our short course on Python for Physics and Astronomy we begin by exploring how Python handle image input and output
Python Imaging Library - PIL
Before we get into the broad area of image processing in Python, there is a caveat for users PIL in Python 3. The essential Python Imaging Library (PIL) is not yet completely compatible with new version of Python. Consequently the FITS tools we will need for astronomical image processing are also currently only supported in the mature versions of Python 2. The comments that follow are based on Python 2.7.
PIL provides functions to manipulate images, including reading, modifying and saving in various standard image formats. Its functions are documented in an on-line manual with a tutorial, and in this handy pdf guide.
As a simple starting example, suppose you have an image that was taken with the camera turned so that "up" is to the side when the image is displayed. Here's how you would rotate an image 90 degrees.
import Image as pil
parser= argparse.ArgumentParser(description = 'Rotate a png image 90 degrees')
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
sys.exit("Usage: png_image_rotate file.png ")
exit()
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
infilename = sys.argv[1]
else:
sys.exit("Usage: png_image_rotate file.png ")
exit()
myimage = pil.open(infilename) mirror = myimage.transpose(pil.ROTATE_90) outfilename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(infilename))[0]+'_r90.png' mirror.save(outfilename)
The first part of this is standard form to get the image name on the command line and make it available to the program. The PIL is imported with Image, and appears in the code as
"pil". This is an amazingly short program, because in opening the image the library handles all the conversions in formatting and stores the image internally so that you refer to it only by the name assigned when it is loaded. We operate on the image with the transpose function, which has an argument that controls what it does. Here we rotate the image 90 degrees, and then save it to a file with a new name. The saving operation converts the internal data back to the file format set by the extension used in the file name.
You can transpose an image left-right with
mirror = myimage.transpose(pil.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
or do both in one step with
mirror = myimage.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT).transpose(pil.ROTATE_90)
Processing is not limited to "PNG" files, though that file type is preferred because it is not a lossy storage option. Python reads and writes "jpg" files too. While PIL provides some essential functionality, for more practical uses in astronomy we need to read Flexible Image Transport or "FITS" files, and to enable numerical work on images in SciPy.
SciPy image processing
SciPy can read jpg and png images directly, without using PIL. With SciPy images are stored in numpy arrays, and we have direct access to the data for uses other than visualization.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.misc import imread, imsave
image_data = imread('test.jpg').astype(np.float32)
print 'Size: ', image_data.size
print 'Shape: ', image_data.shape
scaled_image_data = image_data / 255.
plt.imshow(scaled_image_data) plt.show()
exit()
For our 512x512 color test image, this returns
Size: 786432 Shape: (512, 512, 3)
because the image is 512x512 pixels and has 3 planes -- red, green, and blue. When SciPy reads a jpg or png image it will separate the colors for you. The "image" is a data cube. In the imread line we control the data type within the Python environment. Of course the initial data is typically 8 bits for color images from a cell phone camera, 16 bits for scientific images from a CCD, and perhaps 32 bits for processed images that require the additional dynamic range.
We can display images with matplotlib.pyplot using imshow() --
imshow(X, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None, interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, origin=None, extent=None, **kwargs)
where "X" is the image array. If X is 3-dimensional, imshow will display a color image. Matplotlib has a tutorial on how to manage images. Here, we linearly scale the image data because for floating point imshow requires values between 0. and 1., and we know beforehand that the image is 8-bits with maximum values of 255.
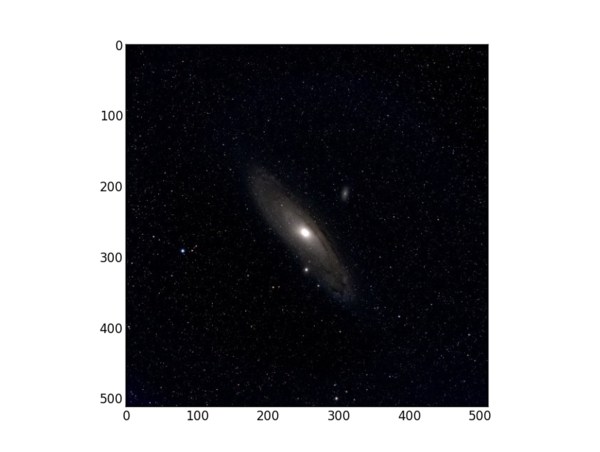
Here's what a single test image displayed from this program looks like in Python.
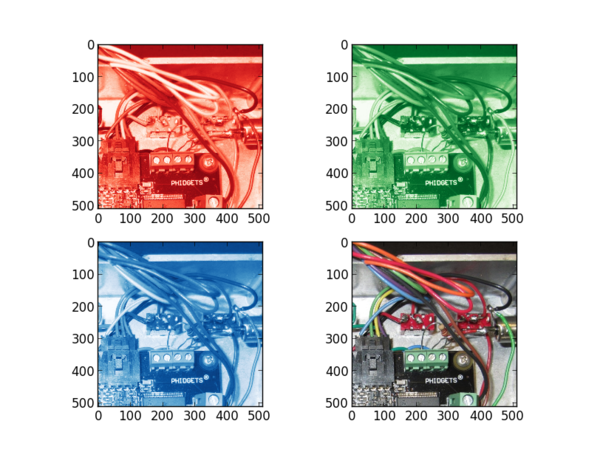
We can slice the image data to see each color plane by creating new arrays indexed from the original one.
import numpy as np from scipy.misc import imread, imsave import pylab as plt
image_data = imread('test.jpg').astype(np.float32)
scaled_image_data = image_data / 255.
print 'Size: ', image_data.size print 'Shape: ', image_data.shape image_slice_red = scaled_image_data[:,:,0] image_slice_green = scaled_image_data[:,:,1] image_slice_blue = scaled_image_data[:,:,2]
print 'Size: ', image_slice_0.size print 'Shape: ', image_slice_0.shape
plt.subplot(221) plt.imshow(image_slice_red, cmap=plt.cm.Reds_r)
plt.subplot(222) plt.imshow(image_slice_green, cmap=plt.cm.Greens_r')
plt.subplot(223) plt.imshow(image_slice_blue, cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
plt.subplot(224) plt.imshow(scaled_image_data)
plt.show()
For a colorful image you will see the differences between each slice --
Astronomical FITS files with PyFITS
PyFITS is available from the Space Telescope Science Institute, and can be added easily to a Python installation that already has NumPy and SciPy. As of January 2013, the current version 3.1.1 of PyFITS supports all the functions needed to manage image and table data in the standard Flexibile Image Transport System (FITS) files of astronomy.
Once a FITS file has been read, the header is accessible for reading, and the image data are available in a numpy array.
Displaying a FITS file in Python
There are many image display tools for astronomy, and perhaps the most widely used is ds9 which is available for Linux, MacOS, and Windows, as well as in source code. It is useful to have a version on your computer when you are working with FITS images. However, sometimes we want to view an image while we are processing it in Python, and for that we could use a routine such as this one.
import os import sys import argparse import numpy as np import pyfits import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot
Sometimes submodules are not loaded with the larger package, and we explictly ask for pyplot.
# Define a function for making a linear gray scale
def lingray(x, a=None, b=None):
"""
Auxiliary function that specifies the linear gray scale.
a and b are the cutoffs : if not specified, min and max are used
"""
if a == None:
a = np.min(x)
if b == None:
b = np.max(x)
return 255.0 * (x-float(a))/(b-a)
# Define a function for making a logarithmic gray scale
def loggray(x, a=None, b=None):
"""
Auxiliary function that specifies the logarithmic gray scale.
a and b are the cutoffs : if not specified, min and max are used
"""
if a == None:
a = np.min(x)
if b == None:
b = np.max(x)
linval = 10.0 + 990.0 * (x-float(a))/(b-a)
return (np.log10(linval)-1.0)*0.5 * 255.0
These functions may be used to rescale the data for display. Scaling can be done with a colormap, or by modifying the data before displaying. Here, we modify the data and save it in a temporary buffer for display. In a more elaborate program with a full user interface, this scaling could be done interactively.
# Provide information to the argparse routine if we need it parser= argparse.ArgumentParser(description = 'Display a fits image')
The argparse function offers more flexibility than the system routines, though here we only include this for future additions.
# Test for command line arguments
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
sys.exit("Usage: display_fits infile.fits ")
exit()
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
infits = sys.argv[1]
else:
sys.exit("Usage: display_fits infile.fits ")
exit()
# Open the fits file and create an hdulist inhdulist = pyfits.open(infits)
# Assign the input header in case it is needed later inhdr = inhdulist[0].header
# Assign image data to a numpy array image_data = inhdulist[0].data
The header and data are now available. We'll look at header information later. For now, all we need are the values in the numpy data array. It will be indexed from [0,0] at the upper left of the data space, which would be the upper left of the displayed image.
# Print information about the image print 'Size: ', image_data.size print 'Shape: ', image_data.shape
For this example we use linear scaling.
# Show the image new_image_data = lingray(image_data) new_image_min = 0. new_image_max = np.max(new_image_data) matplotlib.pyplot.imshow(new_image_data, vmin = new_image_min, vmax = new_image_max, cmap ='gray') matplotlib.pyplot.show()
# Close the input image file and exit inhdulist.close() exit ()
It would be a straightforward exercise to add an interactive scale control and to read out the value of each pixel in this program. With that, it has the basic functionality of ds9.
Flipping an image up/down and left/right
Since images are stored as arrays, there are some simple one-line ways to modify them. Flipping an image top to bottom or left to rignt is done with
numpy.flipud(image_data) numpy.fliplr(image_data)
While we also have to add lines to read the file, update the header, and write it out again, the program to preform these operations is remarkably short. A template program is given in the examples below.
Image rotation is somewhat more complex since it requires tranforming an image in a way that does not preserve its shape, or even the number of elements. We will consider this with the help of SciPy later.
Dark subtraction and flat fielding
There are processing operations done on all "raw" astronomical images taken with charge coupled device cameras. Since the voltage that is digitized is proprotional to the number of photons that arrived at each pixel during the exposure, the data for that pixel should be proportional to the photon count, that is to the irradiance of photons/area-time times the area of the pixel times the exposure time. An absolute conversion to the flux from the sources that are imaged requires correcting for
- Signal at each pixel with no light present -- the "dark" image
- Signal at each pixel for the same irradiance/pixel -- the "flat" field
- Non-linear responses
- Absolute calibration to energy based on spectral response
We can do all of these in NumPy using its built-in array math. By taking an image with no light and subtracting it from an image we have corrected for the dark response (as well as for electronic "bias"). Or, if needed, we can scale a dark image taken at a different exposure time from the image we are measuring, and then subtract that. We can divide an image by a reference flat to correct for pixe-to-pixel variations in response, for vignetting in an optical system (the non-linear fall-off of transmission across the field of view). We can scale images non-linearly to correct for non-linear amplifier responses and saturation or charge loss from each pixel.
For dark subtraction we take the difference of two images:
dark_corrected_image = raw_image - reference_dark_image
and for flat field correction we divide
final_image = dark_corrected_image / reference_flat_image
In NumPy there is no array indexing needed, and the operations are one-liners.
The reference images must be obtained beforehand. For example, a reference dark image may be a median average of many images taken with the same exposure time as the science image, but with the shutter closed. To perform the median operation on the arrays rather than sequentiall on the elements, we stack all of the original individual dark images to make a 3-d stack of 2-d arrays. For example
dark_stack = np.array([dark_1, dark_2, dark_3])
where dark_1, dark_2, and dark_3 are the original dark images. We need at least 3, or any odd number in the dark stack. If the images are m rows of n columns, and if we have k images in the stack, the stack will have a shape (k,n,m): k images, each of n rows, each of m columns. A median on the first axis of this stack returns the median value for each pixel in the stack --
dark_median = np.median(dark_stack, axis=0)
and has a shape that is (n,m) with the elements that we wanted.
Median operations on a image stack remove random noise more effectively than averaging because one source of noise in CCD images is cosmic ray events that produce an occasional large signal at a pixel. If we mean-averaged that data for that pixel the result would be too large because of the one singular event in the stack, but by median-averaging we discard that event without adversely affecting the new reference frame.
A median of a stack of flat frames, all normalized so that they should be identical, will remove stars from the reference image as long as each contributing flat image in the stack is taken of a different star field. Typically, these "sky flats" are images taken at twilight, processed to remove the dark signal, normalized to unity, and then median averaged to remove stars and reduce random noise.
Fortunately, normalizing an image is very simple because
image_mean = np.mean(image_data)
returns the mean value of all elements in the array. Divide an image by its mean to create a normalized image with unity mean
normalized_image = image_data / image_mean
As long as the images have the same size you can sum them by simple addition
sum_image = image1 + image2 + image3 ...
We would do this to create a final image that is effectively one long exposure, the sum of all the contributing image exposure times. Because of guiding errors, cosmic rays, and weather one very long exposure is often not possible, but 10's or 100's of shorter exposures can be "co-added" after selecting the best ones and aligning them so that each pixel in the contributing image corresponds to the same place in the sky.
Finally, for spectroscopy the useful data in an image may be a sum over a region. In that case we could index through the array and explicitly create the sum if needed, but in the ideal case of a spectrum we may want only the sum along a column for each element of a row. For that, the function is
spectrum = np.sum(image, axis)
which returns a numpy array that is the sum along the specified axis. If there are regions in the image that should not be included in the sum, then the image could be masked before computing the sum. The result is a 1-d array in which each element is the signal at a different wavelength.
FITS headers
Processing astronomical images
SciKit image processing
Examples
For examples of Python illustrating image processing, see the examples section.
Assignments
For the assigned homework to use these ideas, see the assignments section.