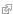Cavendish Experiment Simulator
Simulation
Click into window with the graph to stop and restart the simulation. See the Graph Values and the Experiment Parameters below. If you are new to this, see Explanation of the Cavendish Experiment.
The table below shows the turn around and zero torsion crossing events.
Graph Values Displayed
The values shown in the graph are:
Theta θ: is the deflection angle from the zero torsion angle α0. It correspond to the red arc in the graphic.
Fg1: is the magnitude of the gravitational force between a fixed and a suspended weight according to Newton's law of universal gravitation. Note, this is not the only force that is acting on the suspended mass and only the tangent component of this force incorporates into the total force of the system.
Fg: is the magnitude of all tangential components of the gravitational forces on the weights m2. If kt = 0 and kd = 0 then this is the only force acting in the system.
Ft: is the torsion force due to the torque induced by the string torsion constant kt. In equilibrium and if the weights do not touch each other, it is Fg = Ft.
Experiment Parameters
Change the following values to simulate your configuration:
Speed: defines how much faster the simulations runs than normal speed.
m1, m2: mass of the fixed and suspended weights respectively. See Gravitational Forces how the masses create a gravitational force which moves the suspended weights.
r1, r2: radius of the fixed and suspended weights respectively. The size of the weights has no influence on the movement of the suspended weights. They only define the collision angles.
L1, L2: distances of the fixed and suspended weights from the pivot.
kt: string torsion constant that incorporates a torque due to the twisting of the string from the zero torsion angle
kd: factor to incorporate a linear damping, so that the system does not oscillate infinitely. Real physical systems often have linear and quadratic damping factors. Linear damping means, that the damping force is proportional to the speed. Quadratic damping means, that the damping force is proportional to the square of the speed. Quadratic damping needs only be taken into account for fast moving system. See Drag Force how this parameter results in a force damping the oscillation of the suspended weights.
α0: is the angle of zero torsion in the supporting string.
θ0: is the initial deflection angel as measured counter clockwise from α0.
Explanation of the Cavendish Experiment
The Cavendish experiment uses two fixed weights and two weights on the ends of a bar which is suspended on a string so it can rotate around a pivot. This setup cancels the influence of earth's gravity on the experiment. If you place the big fixed weights near the small weights, they attract each other. Because the involved forces are tiny the movement is very slow and it can take a long time to see a result, at least some minutes to hours. Because the gravitational forces between the weights are so tiny, the experiment has to be shielded from air currents and electric and magnetic influences.
The Cavendish balance experiment can be used to measure the gravitational constant G by following these steps:
- Computing the Moment of Inertia for the Suspension Bar
- Measuring the String Torsion Constant if not already known.
- Measuring the Gravitational Force between the weights in equilibrium
- Computing the Gravitational Constant G
To be able to execute steps 3 and 4 you have to design the setup in such a way that the weights do not touch in equilibrium. The string torsion force has to be strong enough to counteract the attraction between the masses. In equilibrium the force due to the string torsion is equal the gravitational attraction. So knowing the string torsion constant kt and the deflection angle θ due to gravity we can compute the torsion force Ft, which is equal the gravitational attaction Fg of the weights. From the distance of the weights in equilibrium, the measured gravitational forces and the mass of the weights we can compute the gravitational constant G.
To demonstrate that mass attracts mass without quantitatively measure the forces, you can setup the experiment so, that the weights simply collide. In this case you have not to deal with the string torsion force, as long as it is not strong enough to hold the weights seprarated.
How does the Simulation help?
This is a simulation of a simple Cavendish experiment setup. It can be used to estimate how long it takes until the gravitational forces between the weights lets them collide. It explains and simulates how the string torsion constant can be measured and how the gravitational forces can be obtained from that and how G can be calculated then.
It is assumed that the moving weights are suspended on a string at the center pivot. If twisted, the string can exert a torque that counteracts gravity. The magnitude of the torque is dependent on the deflection angle θ of the suspension bar from the zero torsion position α0 and can be controled by the Parameter kt.
In addition a linear damping force can be applied to the system. The magnitude of the damping is dependent on the angular speed of the suspension bar and can be controled by the Parameter kd.
Simulation of a Commertially available Cavendish Experiment
A physics lecture demonstration used at Harvard University is based on a commercial apparatus for teaching about the Cavendish Experiment. This is the same equipment we use in our teaching laboratory and that will be incorporated into the online Introductory Physics laboratory classes.
They give the details about the apparatus and results to be expected in a demonstration, like the final equilibrium angle and the oscillation period. You can reproduce that behavior with this simulator.
Set Simulation State for the Harvard Demonstration Experiment
Measuring the String Torsion Constant
If you create the Cavendish experiment yourself, you probably don't know the string torsion constant kt. But you can measure it using the following method:
- Remove the fixed weights m1
- Let the suspension bar find its zero torsion position α0
- Displace the suspension bar some degrees from α0
- Let the suspension bar oscillate
- Note the times when the bar reaches its maximum deflection angles
(Jump directly to the formula (5) if you have already measured T to compute kt)
The idea behind this is: The string acts like a spring and the suspension bar like a mass. So we have a spring-mass system that can oscillate. The torsion constant corresponds to the spring constant. The only difference is, that we have a rotating system, where the torsion constant gives a torque rather than a force and the mass is replaced by a moment of inertia.
The oscillation period of a mass-spring system can be computed as follows:
| (1) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
Note that the period is measured from one point of oscillation until it reaches the same point from the same direction.
Tip: If you have multiple time periods measured in one run, average over the last few periods, because the influence of damping and non-linearities in the system is smallest when the amplitude of the oscillation is smallest.
The oscillation period of a string-suspension bar system can be computed very similarly:
| (2) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
If we have measured the oscillation period T, we can compute the corresponding string torsion constant by solving (2) for kt:
| (3) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
But what is this Moment of inertia I? It is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis; similar to how mass determines the force needed for a desired linear acceleration.
The moment of inertia depends on the mass distribution of an object. Is can be computed by dividing an object into many small volume elements mi. The moment of inertia of each element is its mass times the square of its distance from the rotation axes: Ii = mi · ri2.
For a suspension bar with heavy weights at the end, so that the weight of the bar is negligible, like in the simulation, the moment of inertia is simply:
| (4) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
See Computing the Moment of Inertia for the Suspension Bar, if the mass of the bar itself is not neglegtable or if you want higher precision measurements.
So for the suspension bar system in the simulation or for a corresponding real model we can compute the string torsion constant by inserting (4) into (3):
| (5) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Example Measuring the String Torsion Constant
Set Simulation State for this Example
To measure the string torsion constant we remove the fixed weights. Then we displace the suspension bar from the zero torsion angle (the rest position α0) some degrees eg. θ0 = 1° and let the suspension bar oszillate. We stop the time T of one full oszillation.
Note: due to damping and some non-linearities in the suspension string the most accurate measurement for T is when the oszillation angle is as small as possible. But this can make it difficult to stop the time accurately. One way to get better results is to average over some periods.
My simulation got me a period T = 6562 s (from the event table below the simulator).
If the weight of the suspension bar is neglegtable with respect to the weights m2, I can directly use formula (5) to calculate the string torsion constant kt:
| (6) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
which is very close to the value kt = 20 × 10−9 N·m/rad that I entered in the simulation for this example.
Computing the Moment of Inertia for the Suspension Bar
To measure the string torsion constant kt with the formula (3) you need the moment of inertia I of the suspension bar with the weights m2. If the weight of the bar itself is much smaller than the weights at the end, you can neglegt the moment of inertia of the bar and simply use (5) to compute kt.
If the mass of the bar is not neglegtable or if you want higher precision measurements, you can incorporate the moment of inertia of the bar itself. Assuming the bar is a rod with any cross section shape, but constant diameter and density, you can compute its moment of inertia as follows:
| (7) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
The total moment of inertia of the suspension bar inclusive the weights at the end is then:
| (8) |
| |||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Note that Lbar is the length of the bar without the weights. So dependent of your construction Lbar may be smaller or bigger than 2 · L2.
If we want to be even more precise we have to include the moment of inertia of the ball weights too, due to their rotation. But beacuse the rotation is so slow, I did ignore it. But here is the contribution listed anyway:
| (9) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
So the total moment of inertia gets:
| (10) |
|
Measuring the Gravitational Force
To measure the gravitational force it is not sufficient to simply let the weights come together. You have to setup the system in such a way, that the weights come closer but never touch. Wait until the oscillation stops. Now you can measure the angle θ from the zero torsion position α0 to the current position. In this equilibrium state the momentum due to the string torsion is proportional to the gravitational force.
If we now the string torsion constant kt and the angle θ we can compute the torque and from that the corresponding torque forces at the positions of the 2 weights m2. In equilibrium the sum of this forces is just equal to the total gravitational force:
| (11) |
| |||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Now we have the sum of all tangential acting components of the gravitational forces Fg as displayed in the simulator. The force acting at one mass is half of that.
To compute the gravitational constant we need not the total tangential components of the gravitational forces but the force vector from one mass m2 to the nearest mass m1. We have essentially to reverse engineer what the simulation does as described at Gravitational Forces to get
But we can use Fg as an approximation:
| (12) |
To get the real force
The real force is then:
| (13) |
| |
| with | ||
| and |
Computing the Gravitational Constant G
The formula to compute a gravitational force between two weights is:
| (14) |
If we know F, the masses and the distance d between the weights, we can calculate the gravitational constant G by solving (14) for G:
| (15) |
|
F is our Fg / 2 from Measuring the Gravitational Force.
To check that the formulas are correct, you can use the force displayed as Fg1 in the simulation. This is the pure force between two weights m1 and m2 (not their tangential component).
What we still don't know is the distance d between the weights. We can measure it or calculate it from the deflection angle θ:
| (16) |
Example computing G
Set Simulation State for this Example
In this example I got the following deflection angle after some hours after the suspension bar stoped oscillating: θ = 2.411°. Assuming we have already measured the string torsion constant kt = 20 nN·m/rad, we can compute the torsion force which is the same as the total gravitational forces:
| (17) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Lets calculate the distance between the weights:
| (18) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
The gravitational constant using the measured force F ≈ Fg / 2 is then:
| (19) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
If we use the exact gravitational force as displayed at Fg1 and computable with (13) we get:
| (20) |
| ||||||||||||
| where' |
|
which is the publised value.
Simulation Math
The simulation is based on the physics of the Cavendish experiment. The sum of all forces results in the acceleration of the suspended weights. A Numerical Integration of the acceleration delivers the next state after a small time interval that specifies the new rotation speed and position. From this new state all forces are computed again, and so forth.
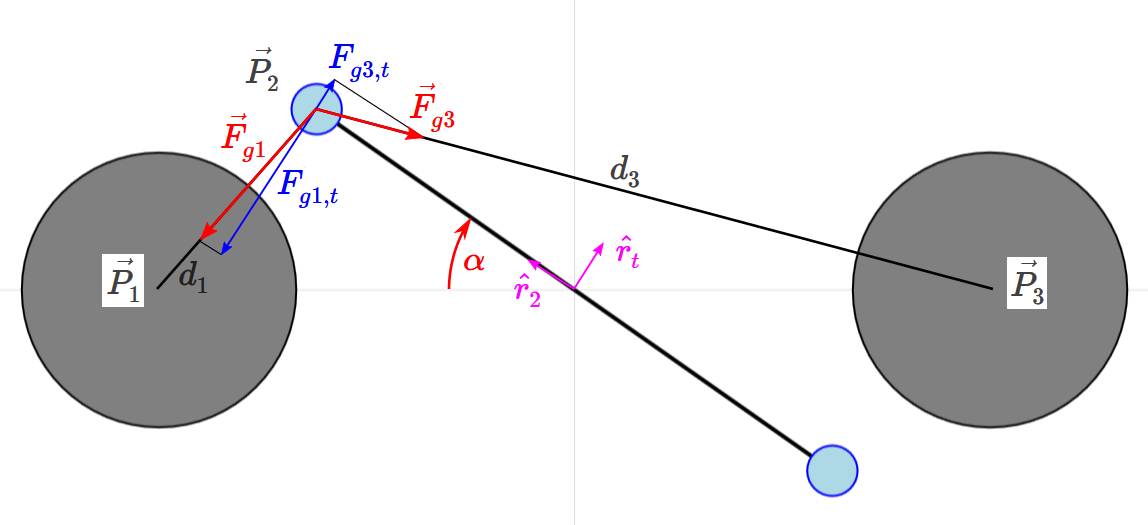
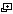
Gravitational Forces
To calculate the gravitational forces we need to define some points as vectors, for which the origin is at the pivot of the weights m2:
| (21) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Furthermore we need the vectors from
| (22) | |||||||
| (23) | |||||||
| (24) | |||||||
| (25) | |||||||
| where' |
|
The gravitational force vectors are then:
| (26) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Note: the term
Because the suspended weights are not free to move in any direction but are constrained to rotate around the pivot point, only the tangent components are relevant for the movement. The radial components of the forces cancel each other. To calculate the tangent components we introduce a tangential unit vector
| (27) |
Now we can calculate the tangential components of the gravitational forces by applying the vector dot product:
| (28) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
To get the total gravitational force we add the tangential force components and multiply by 2 because we have 2 suspended weights:
| (29) |
| ||||||
| where' |
|
The sum of the tangent components of the gravitational forces is displayed as Fg in the simulation.
Note:
Torsion Force
The string exerts a torque on the suspended mass system that is proptional to the rotation angle measured from the zero torsion angle
The magnitude of the torque is:
| (30) |
The torque is acting against the displacement from α0, so the torsion force is minus:
| (31) |
| |||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Note: this is the sum of the two torsion forces acting at each mass m2.
If the torsion constant kt is too big, the gravitaional forces cannot move the weights together, but only deflect them in the corresponding direction. The torsion force is displayed as Ft in the simulation.
Drag Force
To introduce a damping of the system, we can define a linear damping constant kd, which produces a tangential damping force always acting against the direction of motion. The magnitude of the damping force is proportional to the angular speed.
| (32) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
If you set kd = 0 the system is undamped and oscillates indefinitely.
Acceleration
Now we get to the equations of motion. If we know all forces acting on the suspended part of the system, we can compute the angular acceleration applying Newton's second law of motion a = F / m:
| (33) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| where' |
|
Note: to get from the linear acceleration to the angular acceleration, we had to divide by L2.
It is common practice to write accelerations with two dots and speeds with one dot above the angle variable. One dot means a differentiation with respect to time. Two dots mean two times differentiated with respect to time.
Equation of motion
From the angular acceleration we can calculate the angular speed by integration:
| (34) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
From the angular speed we get the angel by integration:
| (35) |
| |||||||||
| where' |
|
Numerical Integration
The integration cannot be done analytically for such complicated systems, but have to be done numerically by a computer program.
In principle we divide the motions into small chunks of time length
| (36) | |
| (37) | |
This steps are continuously repeatet for each time step
Note: the simulation uses a more sophisticated rule for the integration, that halves the error compared to the above method.
Collision handling
The weights can collide if the difference of L1 and L2 is smaller than the sum of the radii r1 + r2 of the weights.
If the weights cannot collide, nothing has to be done, the simulation just works. But if the weights can collide, their angular speed has to be reversed on collision detection and the angular position has to be corrected.
We assume an elastic collision. That means the momentum is conserved without energy loss on the collision. This is established by simply inverting the angular speed on collisions.
To check for collisions we need the minimum and maximum angular positions of the suspension, that correspond to the collision positions. We can get the angles geometrically from the triangle P1, Pivot, P2 when the weights touch each other. In this case P1 and P2 are at a distance of r1 + r2 and the other sides of the triangle are L1 and L2:
| (38) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| (39) | |||||||||||||||||||
| where' |
|